El Niño and La Niña – Friend or Foe to the High Risk Homeowners Insurance Market?
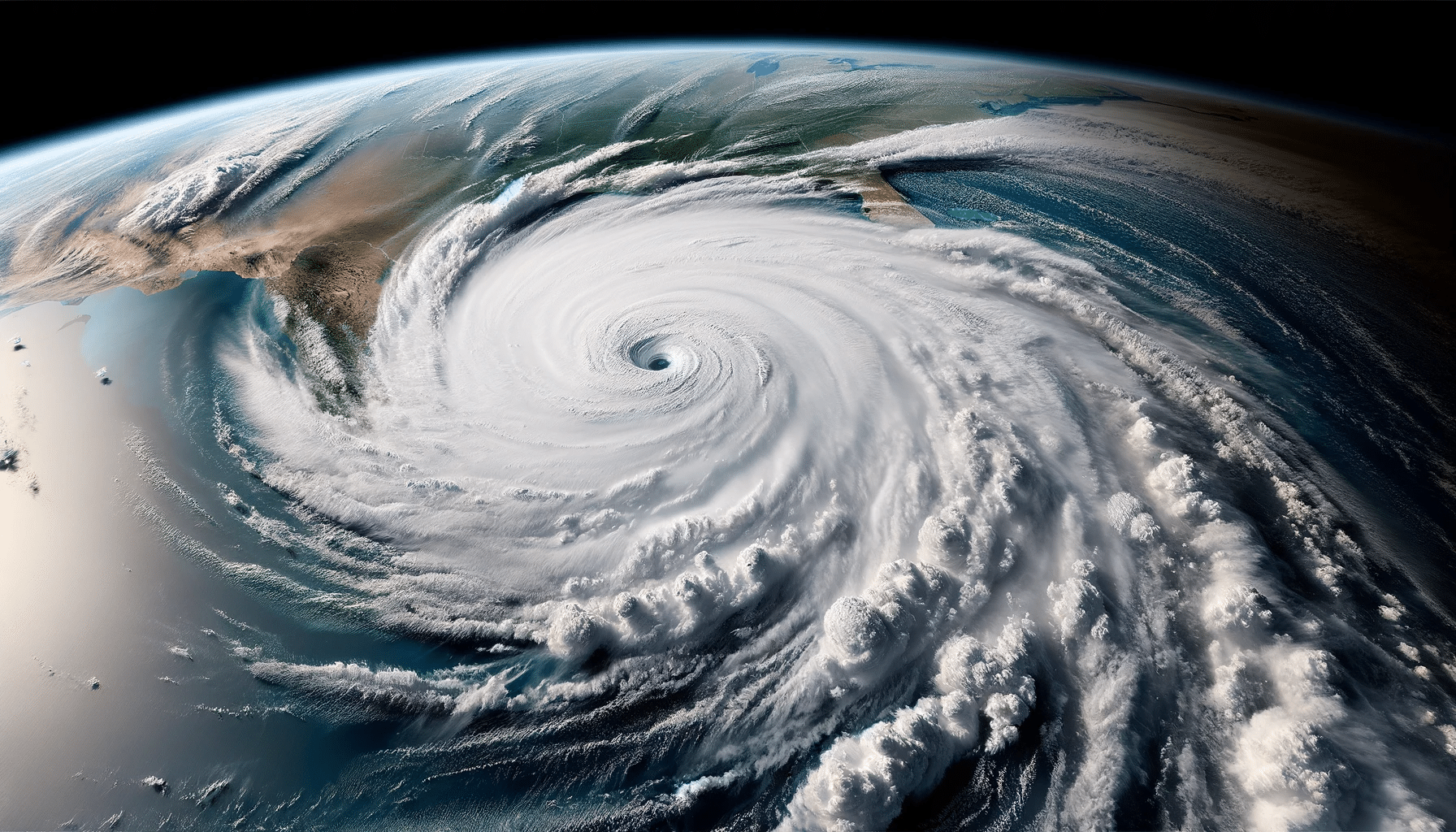
Climate patterns like El Niño and La Niña significantly influence global weather, impacting everything from temperature to marine ecosystems. These phenomena, part of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, can lead to drastic weather changes, affecting economies and environments worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of El Niño and La Niña, exploring their causes, effects, and the science behind these powerful climate drivers.
In 2024, the global climate is expected to transition from El Niño to La Niña. The El Niño event, which peaked between November 2023 and January 2024, is currently weakening and is predicted to shift to neutral conditions around mid-2024. This transition is likely to be followed by La Niña developing in the second half of the year.

What is El Niño?
El Niño is characterized by the periodic warming of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. This phenomenon disrupts normal weather patterns, leading to various global impacts and is a significant concern to the property insurance market.
Causes of El Niño
El Niño occurs when trade winds weaken, allowing warm water to move eastward across the Pacific. This shift in ocean temperature affects atmospheric conditions, altering weather patterns globally.
Effects of El Niño
- Weather Changes: El Niño typically causes wetter conditions in the southern United States and drier conditions in the Pacific Northwest. Globally, it can lead to extreme weather events, such as heavy rains, floods, and droughts which will potentially lead to tens of thousands of additional homeowners insurance claims.
- Marine Life: The warming of ocean waters during El Niño disrupts nutrient upwelling, which affects marine ecosystems. This can lead to reduced fish populations and impact the species that rely on them.
- Economic Impact: Agriculture, fisheries, and water resources are significantly affected by the weather extremes caused by El Niño, leading to economic challenges in affected regions.

What is La Niña?
La Niña is the counterpart to El Niño, characterized by cooler than average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. La Niña is expected to develop between June to August 2024.
Causes of La Niña
La Niña occurs when trade winds strengthen, pushing warm water towards Asia and allowing cold, nutrient-rich water to surface along the Americas’ west coast.
Effects of La Niña
- Weather Changes: La Niña typically brings wetter conditions to the Pacific Northwest and drier, warmer weather to the southern United States. It can also lead to increased hurricane activity in the Atlantic and is one of the likely reasons that 2024 is expected to be an above average hurricane season.
- Marine Life: Enhanced upwelling during La Niña brings nutrients to the surface, supporting marine life and boosting fish populations.
- Economic Impact: Similar to El Niño, La Niña affects agriculture, water resources, and fisheries, with significant economic implications in impacted areas.
Comparing El Niño and La Niña
Both El Niño and La Niña are integral parts of the ENSO cycle, each with distinct impacts on global weather patterns and marine ecosystems. While El Niño tends to bring warmer, wetter conditions to certain regions, La Niña often results in cooler, drier weather. Understanding these patterns helps in predicting and mitigating their effects on our environment and economies.
How to Prepare for El Niño and La Niña
- Monitoring and Prediction: Advances in technology and climate science allow for better monitoring and prediction of these phenomena, helping communities prepare for potential impacts.
- Adaptive Strategies: Implementing adaptive strategies in agriculture, water management, and infrastructure can mitigate the adverse effects of extreme weather associated with El Niño and La Niña.
- Public Awareness: Educating the public about the signs and impacts of these climate patterns is crucial for community preparedness and resilience.
Bottom Line
El Niño and La Niña play crucial roles in shaping our global climate and have severe ramifications in the level of readiness needed for most homeowners who live in high risk areas. By understanding their mechanisms and impacts, we can better prepare for the challenges they pose. As climate patterns continue to evolve, staying informed and adaptive will be key to mitigating their effects on our world.
FAQs
1. How often do El Niño and La Niña occur?
El Niño and La Niña events typically occur every two to seven years, but they do not follow a regular schedule.
2. Can El Niño and La Niña impact global food production?
Yes, the weather extremes caused by these phenomena can significantly affect agriculture, leading to crop failures and impacting food security.
3. Are there regions more affected by El Niño or La Niña?
Yes, regions like the southern United States, Pacific Northwest, and parts of South America are more affected by the weather changes induced by these patterns.
4. How do scientists predict El Niño and La Niña events?
Scientists use oceanic and atmospheric data, along with climate models, to predict the onset and intensity of El Niño and La Niña events.
5. Can El Niño and La Niña influence global temperatures?
Yes, these climate patterns can influence global temperature averages, contributing to periods of warming or cooling.
By understanding El Niño and La Niña, we can better anticipate and mitigate their profound impacts on our weather, ecosystems, and economies.
Recent Posts
2024- Are Burglary Claims Still a High Risk?
Burglaries are a persistent threat to homeowners across the U.S., with over one million break-ins occurring annually. Even though burglary rates have decreased...
2024 Atlantic Hurricane Season Predictions
All Early Predictions Call for a Busy 2024 Atlantic Hurricane Season Forecasters are predicting an exceptionally active Atlantic hurricane season in 2024. The...
Top High-Risk Home Insurance Factors
When you own a home, one of the most important things you need is home insurance. This insurance helps protect your house and...




